
- #Osx format external drive for mac#
- #Osx format external drive install#
- #Osx format external drive full#
- #Osx format external drive software#
Next, connect your Windows drive to the Mac. Press Ctrl+O to save the list, and then press Ctrl+X to exit NANO. USB1 (if you’re unsure what this is, simply open Disk Utility): LABEL=NAME none ntfs rw,auto,nobrowse Use the arrow keys on your keyboard to scroll to the very end and add the following line, replacing ‘NAME’ with the actual name of your NTFS drive e.g. This will open the list of drives recognised by macOS. Connect your NTFS drive, then enter the command: sudo nano /etc/fstab To get started, click the Spotlight icon at the top right of your screen and enter ‘Terminal’. As this feature is still in the testing phase however, your files could become corrupted at anytime, so proceed with caution.
#Osx format external drive software#
The main benefit of using Terminal in this way is that it’s quick to do and no third-party software is required.
#Osx format external drive full#
This is an experimental feature and could lead to data loss, so make sure to do a full backup of both your Mac and any data on the drive before continuing.
#Osx format external drive for mac#
If reformatting your NTFS drive for Mac is not an option, you can enable write support for specific Windows disks using macOS Terminal. From now on you’ll be able to move files to your drive and edit them in place from a Mac or PC. Read the warning carefully before proceeding, as this process will delete any existing data on the drive. Enter a new name for the drive in the field above if you wish.Ĭlick ‘Erase’ to continue. Insert your NTFS drive or USB stick and click to highlight the disk name in the white box on the left-hand side of the window. To get started, click the Spotlight icon at the top right of your screen and enter ‘Disk’ to launch Disk Utility. More information on FAT32 versus NTFS is available from Microsoft Support. This may pose a problem if you’re using the drive to store high-quality videos. This is simple to do and means the data on your drive/USB stick can be read and written on both Macs and PCs.īe aware that the FAT32 format isn’t as efficient as NTFS: it only supports files sizes of up to 4GB.
#Osx format external drive install#
Step 1: Download and install AweCleaner for Mac on your Mac.If you have an NTFS drive you can use macOS’ Disk Utility to reformat it to FAT32. Solution 2: format hard drive under macOS 10.13 High Sierra with AweCleaner for Mac Please note that the formatted data on your hard drive still can be recovered by data recovery software. Step 8: Plate Utility will begin organizing the drive. Select the non-indented section for your Seagate drive.Ĭautioning: Formatting the drive will eradicate all data on the drive, so you should duplicate any data you need off the drive before arranging. Tap on the view catch in the upper left-hand side, change to Show All Devices. Note: If you don't see the plan choice, at that point you have chosen the volume and not the drive.

Step 6: Select GUID Partition Map for Scheme Step 5: Select OS X Extended (Journaled) for Format
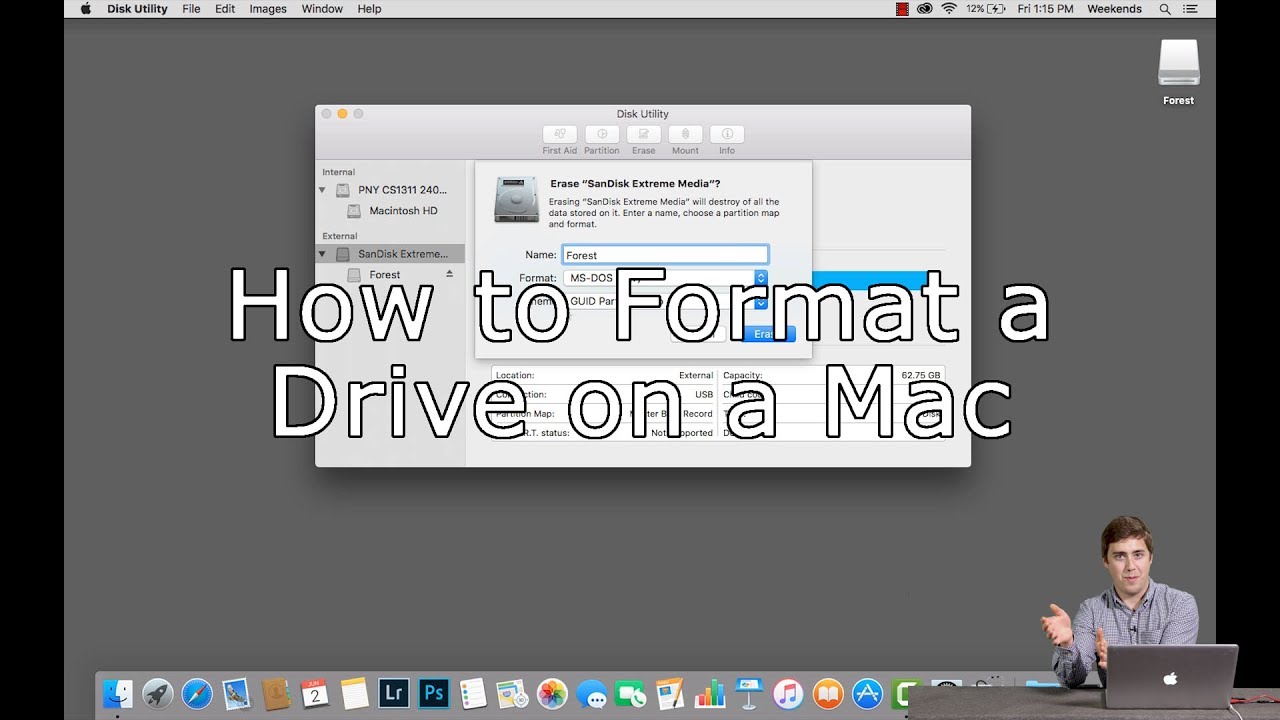
Step 3: Select ‘Erase ‘ which opens the accompanying window. This component was presented in macOS 10.13 High Sierra The view catch is in the upper left-hand side, change to Show All gadgets. Note: If you don't see two passages filed at that point change the view in plate utility to demonstrate the drive and the volume. Step 2: Select the hard drive on the left. Open Finder > Applications > Utilities > Disk Utility Solution 1: format hard drive under macOS 10.13 High Sierra with Disk Utility Now, let's start to format a hard drive under macOS 10.13 High Sierra with some easy tools. First of all, get your data backed up before do the format. In this article, we will introduce you a few tools you can use for formatting hard drive under macOS 10.13 High Sierra. When you have the need to format a hard drive under macOS 10.13 High Sierra, it typically requires the use of third-party hard drive format software like Disk Utility.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
